近期,我院教师卞婷(通讯),研究生麻鼎峰等的研究成果“Constructing of Crystalline CoP/Amorphous CoMoP Coupling Composites for Efficient Water Splitting”在《International Journal of Hydrogen Energy》(中国科学院二区)上发表。
论文简介如下:
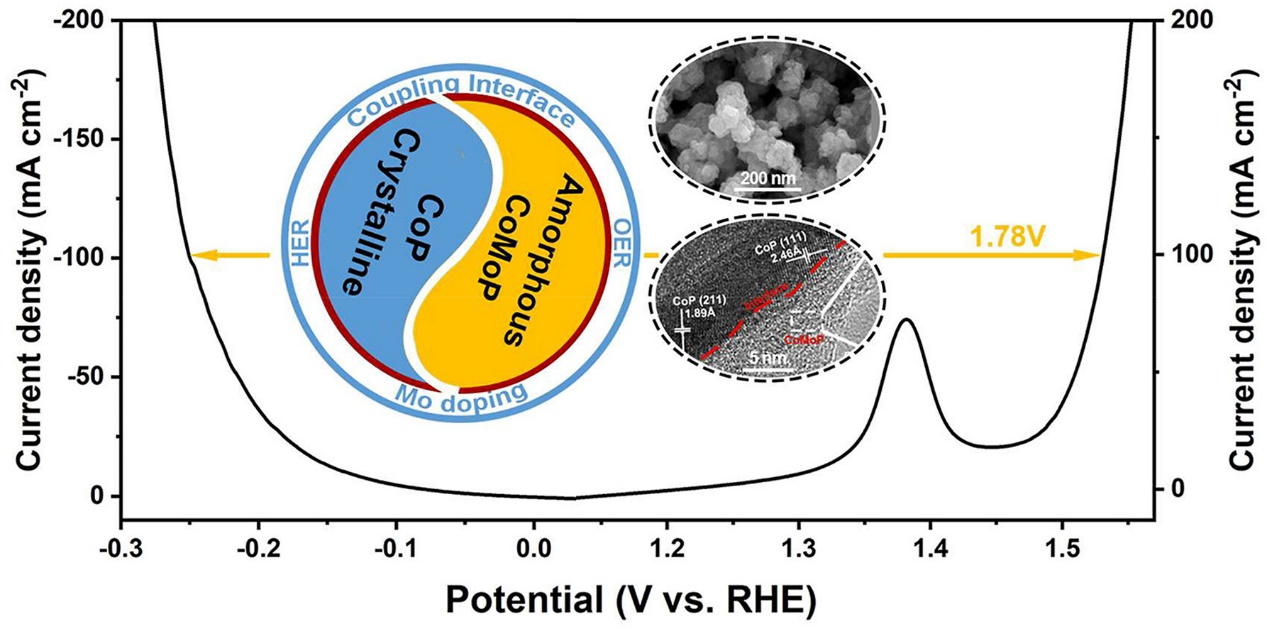
Bifunctional electrocatalysts with the joint merits of being highly efficient,stable, and low-cost are essential for overall water splitting applications. Herein, we reported a unique amorphous/crystalline coupling structure consisting of crystalline CoP nanocrystals with amorphous CoMoP in-situ growth on nickel foam (termed as CoP/a-CoMoP/NF). This was achieved through oxidation-phosphating in two successive steps by Keggin-type POM (H3PMo12O40) embedded into the zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 (ZIF-67) as the precursor. The Mo doping and crystalline/amorphous coupling structures of CoP and CoMoP modulate the electronic structure, increase the electrocatalytic active sites, and promote the interfacial electron transfer, thus accelerating the catalytic kinetics of both the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). The amorphous CoMoP serves a protective role in preventing corrosion during the electrochemical process. The catalyst exhibits low overpotentials of 301 mV and 250 mV to drive a current of 100 mA cm-2 for OER and HER, respectively, and demonstrates excellent stability for both reactions. Furthermore, the alkaline electrolytic cell assembled with CoP/a-CoMoP/NF catalysts as both the anode and cathode requires only 1.66 V and 1.73 V to drive current densities of 50 and 100 mA cm-2, respectively. This study offers a rational strategy for the development of efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for hydrogen generation.
全文下载:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.06.246