近期,我院研究生李静(第一作者),教师苏超(通讯作者)等的研究成果“Zincophilic, Green, Non-Toxic Additives Modulate Lean-Water Inner Helmholtz Layer for Enhanced Stability of Zinc Anodes”在《Energy & Environmental Materials》(IF=14.1)上发表。
论文简介如下:
传统水系电解液中,游离水分子优先吸附在锌负极表面,形成内亥姆霍兹平面(IHP)。富水的IHP通常会诱发无法控制的锌枝晶、析氢反应和腐蚀问题,从而严重影响锌负极的循环寿命。本研究通过采用绿色无毒的二丙二醇二甲醚(DMM)作为电解液添加剂来重塑IHP。DMM具有亲锌性,能优先吸附在锌负极表面,占据IHP。同时,DMM含有两个疏水甲基,可以排斥去溶剂化后残留的游离水分子,构建一个贫水IHP,隔绝水分子与锌负极持续接触。石英微晶天平可以准确地反映 DMM分子在锌负极表面的吸附行为,实现了吸附型添加剂从定性分析到定量分析的飞跃。采用DMM添加剂电解液的Zn//Zn对称电池在0.5 mA cm-2、0.5 mAh cm-2的条件下,循环寿命稳定在2500 h以上。此外,使用 DMM添加剂电解液的Zn//PANI全电池在1 A g-1电流密度下可循环使用1000次,且容量保持率达90%。
In conventional aqueous electrolytes, free water molecules are preferentially adsorbed on the surface of the zinc anode, forming an inner Helmholtz plane (IHP).Water-rich IHPs typically induce uncontrollable zinc dendrites, hydrogen evolution reaction, and corrosion problems that can severely impact the cycle life of zinc anodes. The present study reengineers IHP by employing the green, non-toxic dipropylene glycol dimethyl ether (DMM) as an electrolyte additive.Experimental and computational results show that DMM is zincophilic and can preferentially adsorb on the surface of zinc anode to occupy the IHP. Meanwhile, DMM contains two hydrophobic methyl groups, which can repel free water molecules remaining after desolvation to construct a water-poor IHP and isolate the water molecules from continuous contact with the zinc anode. The quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation test intuitively and accurately reflected the adsorption behavior of DMM on the surface of zinc anode, and realized the leap from qualitative analysis to quantitative analysis. The Zn//Zn symmetric cell with DMM electrolyte have a stable cycle life of over 2500 h at 0.5 mA cm-2, 0.5 mAh cm-2. In addition, Zn//PANI full battery with DMM electrolyte can be cycled 1,000 times with 90% capacity retention under 1 A g-1.
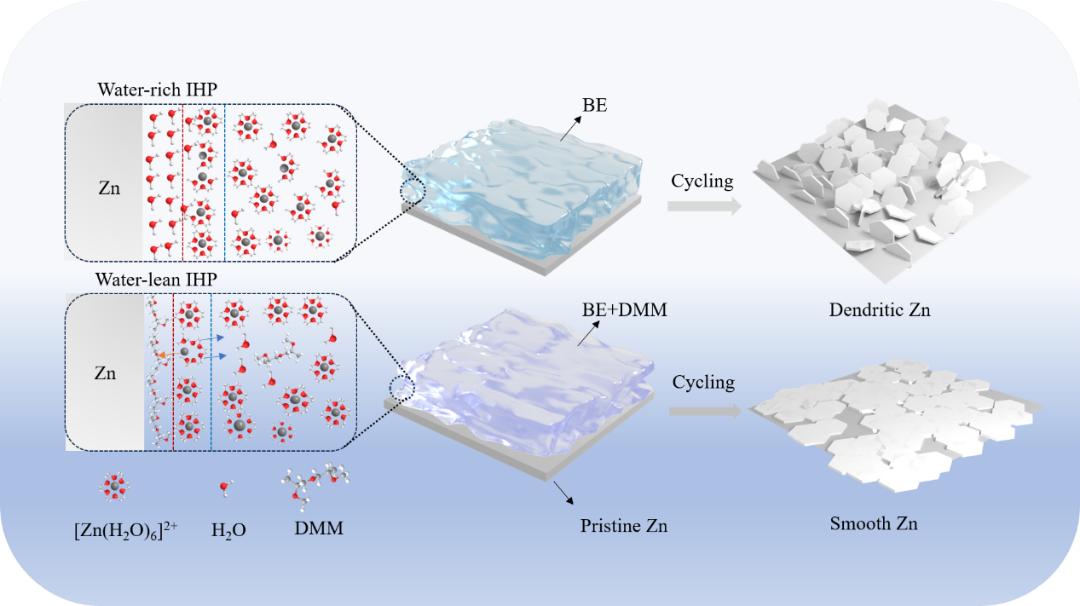
Design strategy of DMM additive for reconstructing a lean-water IHP. In the conventional zinc salt solution, free water molecules in the electrolyte occupy the IHP, leading to severe zinc dendrites and side reactions such as HER and corrosion. The introduction of DMM molecules can quickly occupy the IHP, and Zn2+ can be uniformly deposited on the surface of the zinc anode through electrostatic interactions. At the same time, the hydrophobic methyl group can isolate the direct contact between the free water molecules and the zinc anode surface and inhibit the interfacial side reactions.