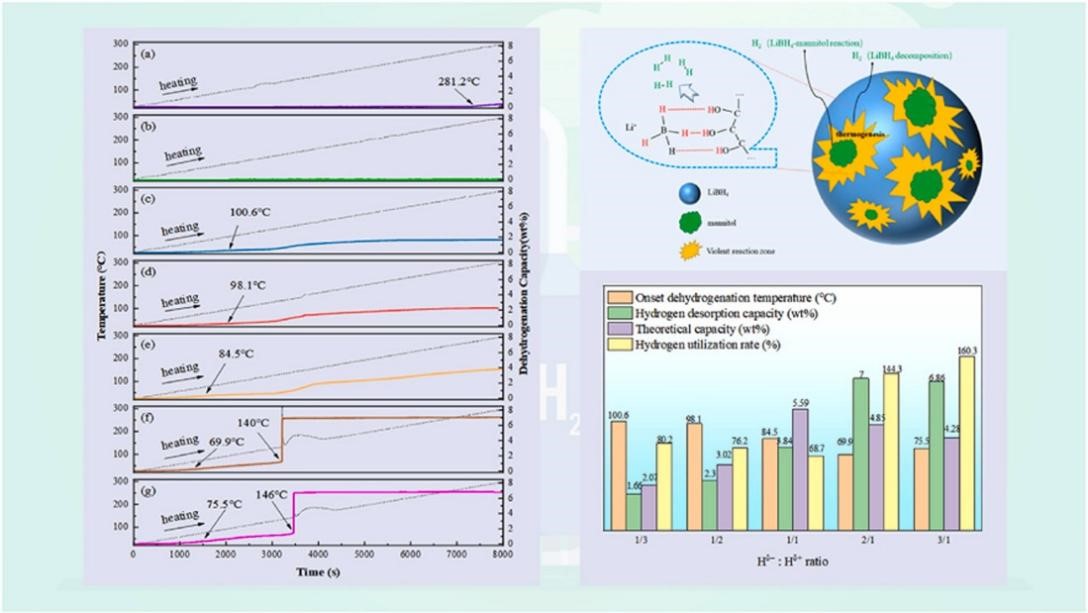
论文简介如下:
在众多储氢材料中,LiBH4由于具有较大的储氢容量而被认为是最佳氢转运载体之一。但是,由于LiBH4热力学稳定,脱氢温度高,难以实现工程应用。本文提出了一种新的方法,用固态甘露醇作为反应物,使LiBH4在69.9 ℃以下脱氢。超过7 wt %的H2可以在140 ℃以下从LiBH4-甘露醇复合体系中快速释放。XRD、FTIR和SEM测试表明,甘露醇(Hδ+)与LiBH4(Hδ−)反应产生氢气的同时产生了大量的热,进一步促进了复合体系中过量LiBH4的分解制氢。这项工作表明了开发基于复杂氢化物的大容量高效制氢系统的可能性。
Among conventional hydrogen storage materials, LiBH4 has been regarded as one of the best hydrogen transporters due to its relatively large hydrogen capacities. However, because of its extraordinarily high dehydrogenation temperatures, LiBH4 was not suitable for hydrogen storage due to its stable thermodynamic features. Herein, we present a novel approach to LiBH4 that uses solid-state multi-hydroxyl mannitol as a reactant, regulating hydrogen release below 69.9 ℃. More than 7 wt % H2 could be released with ultra-fast rates at 140 ℃ from the LiBH4-mannitol composite. XRD, FTIR, and SEM tests revealed that the reaction between mannitol (Hδ+) and LiBH4 (Hδ− ) to produce hydrogen was accompanied by the generation of large amounts of heat in situ, which further promoted the decomposition of LiBH4 for hydrogen production, exceeding the theoretical dehydrogenation amount of Hδ+- Hδ− reaction. This work indicates possibilities for the development of fast and easy high-capacity hydrogen generation systems based on complex hydrides.