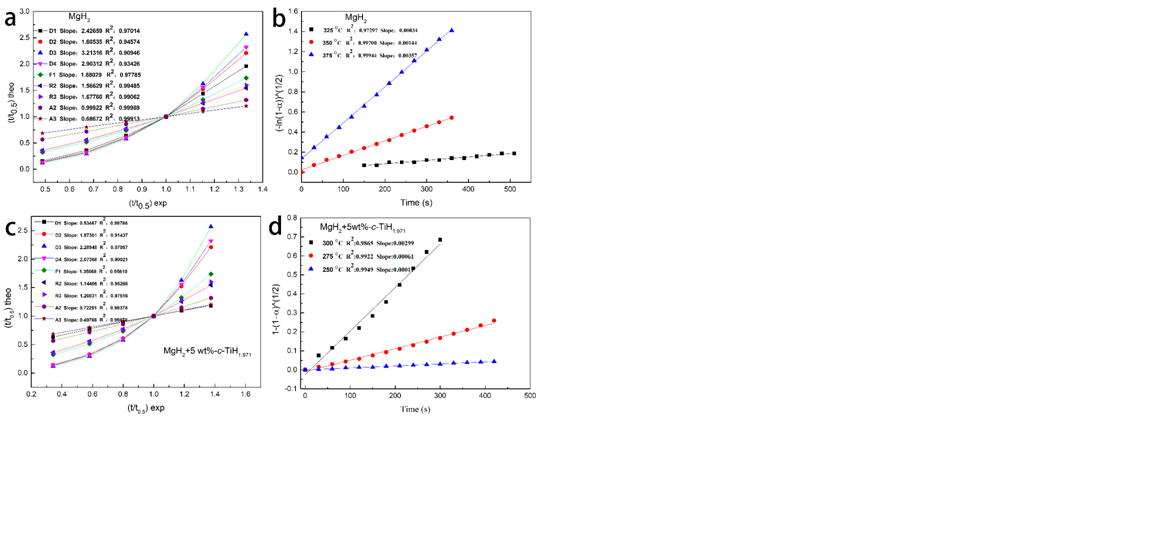
Catalytic doping plays an important role in enhancing the hydrogen storage performance of MgH2, whilefinding an efficient and reversible catalyst remains to be a great challenge in enhancing the de/rehydrogenation properties of MgH2. Herein, a bidirectional nano-TiH1.971 catalyst was prepared by a wet chemical ball milling method and its effect on hydrogen storage properties of MgH2was studied. The results showed that all the TiH1.971 nanoparticles wereeffective in improving the de/rehydrogenation kinetics of MgH2. The MgH2 composites doped withTiH1.971 could desorb 6.5 wt % H2 in 8 min at300 °C, while the pure MgH2 only released 0.3 wt % H2 in 8 min and 1.5 wt% H2 even in 50 min. It was found that the smaller the size ofthe TiH1.971 particles, the better was the catalytic effect on promoting theperformance of MgH2. Besides, the catalyst concentration also played an important role and the 5 wt %-c-TiH1.971 modified system was found to have the best hydrogen storage performance. Interestingly, a significant hydrogen absorption amount of 4.60 wt % H2 was evidenced for the 5 wt %-c-TiH1.971 doped MgH2 within 10 min at 125 °C, while MgH2 absorbed only 4.11 wt% hydrogen within the same time at 250 °C. The XRD results demonstrated that the TiH1.971 remained stable in cycling and could be served as active sites for hydrogen transportation, which contributed to the significant improvement on the hydrogen storage properties of MgH2.
全文下载:https://www.mdpi.com/2079-4991/9/10/1370